

Gregor Mendel, (1822 -1884) was a meteorologist, mathematician, biologist, and Augustinian monk. He was the first person studying genetics scientifically. He has been conducting many experiments involving crossbreeding of pea plants between 1856 and 1863. Mendel is considered as the creator of the science of genetics. He has been explaining scientifically what farmers had known for thousands of years about what may happen when crossbreeding plants, or animals.
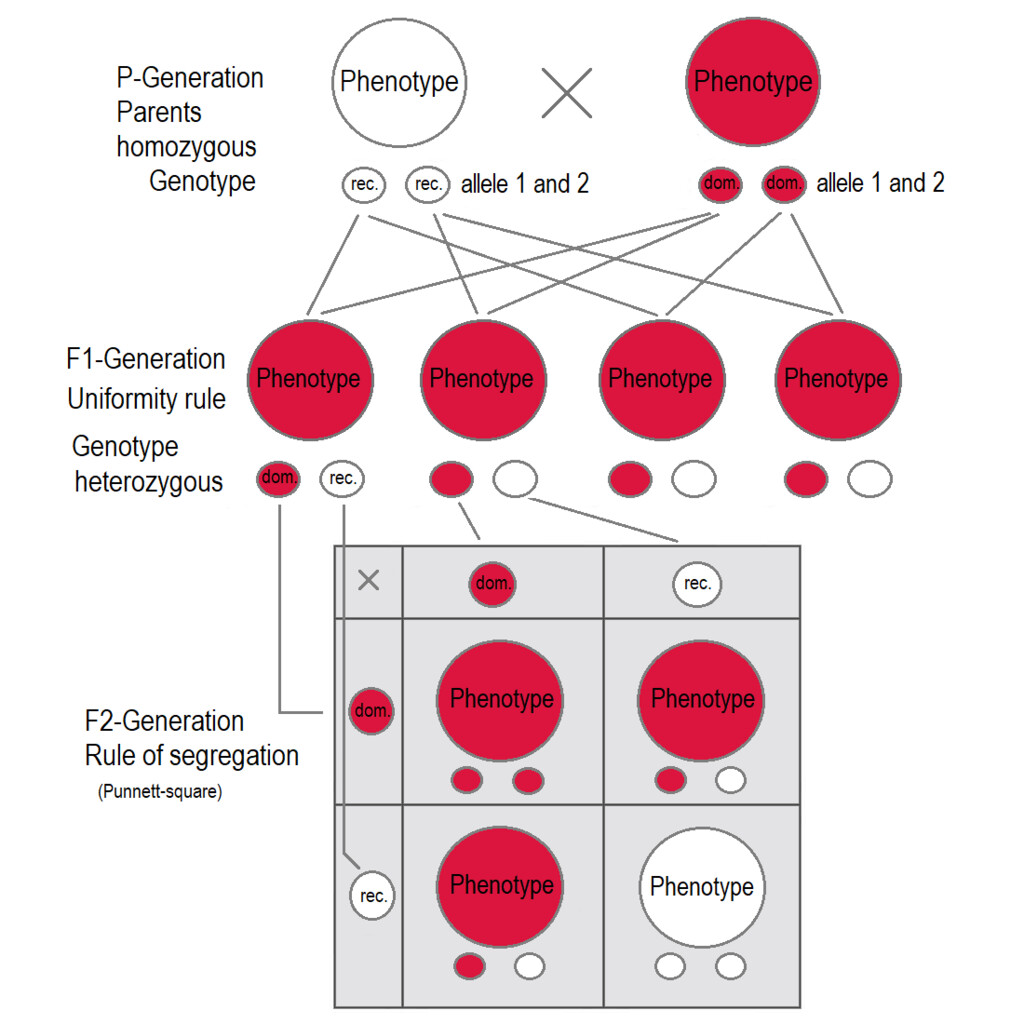
The experiment is starting with crossbreeding the \(P_0\) parent population consisting of two purebred of peas. The first one with white flowers, the second with red flowers. Note that the result of the experiment are of statistical nature.
Result 1: The first generation children \(F_1\) consist of red flowered peas only!
Result 2: The second generation children \(F_2\) consists of \(75\%\) red flowered peas and and \(25\%\) white flowered peas!
It is looking like the red colour is stronger than the white one. When crossbreeding pure white peas with pure red peas, each child of the first generation will get exactly one white allele and one red allele from ist parents. We say here that the red allele is dominant, and that the white allele is recessive. Red is what we see. This is also called the phenotype of the organism. The red colour of the first generation peas is only a visible aspect. In fact, the pea is genetically red and white at the same time. Will call this complete information genotype of the organism.
When mating the first generation children, a quarter of the children will get two red alleles, half of them will get a red allele and a white allele, resulting in a red phenotype. The last quarter will get two white alleles. If both alleles of a child are the same, the say that organism is homozygous, otherwise it is heterozygous. Note that the quantities given here are not exact. They are the results of statistical measurements.

Mendel has been making more experiments involving seven characteristics of peas: seed shape, flower colour, seed coat tint, pod shape,, unripe pod colour, flower location, and plant height. He could derive following three fundamental laws2 of genetics
Some alleles are dominant while others are recessive; an organism with at least one dominant allele will display the effect of the dominant allele.
During gamete formation, the alleles for each gene segregate from each other so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene.
Genes of different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes (sex cells).
A Mendelian trait is one that is controlled by a single gene. In such cases, a mutation in a single gene can cause a disease that is inherited according to Mendel's principles. Dominant diseases manifest in heterozygous individuals. Recessive ones are sometimes inherited unnoticeably by genetic carriers. An important example in Africa is sickle cell anemia3. Note that the recessive gene SCT3 responsible for the trait is protecting humans against malaria infection. The places where malaria is most common are also the places that have the highest percentage of people with SCT.
Wikipedia. Gregor Mendel (last visited Apr. 23, 2022).
Wikipedia. Mendelian Inheritance (last visited Apr. 24, 2022).
Wikipedia. Sickle Cell Anemia (last visited Apr. 23, 2022).
SCD. Sickle Cell Anemia (last visited Apr. 24, 2022).
Prof. Dr. Jacques E. Boillat is a retired professor for Computer Sciences. Jacques E. Boillat has been studying Mathematics, Theoretical Pysics, and Philosophy at the University of Berne, in Switzerland. He has been teaching at the University of Applied Sciences in Berne and at the University of the Gambia from 2006 to 2020. His wife Lenna Correa Boillat is owner of the Shepherd's Farm in Bato Kunku.